We wanted to find out what is the greatest problem geospatial experts face when trying to share raster maps or drone imagery.
So, last year we held a poll for a crowd of GIS power-users. Take a look.
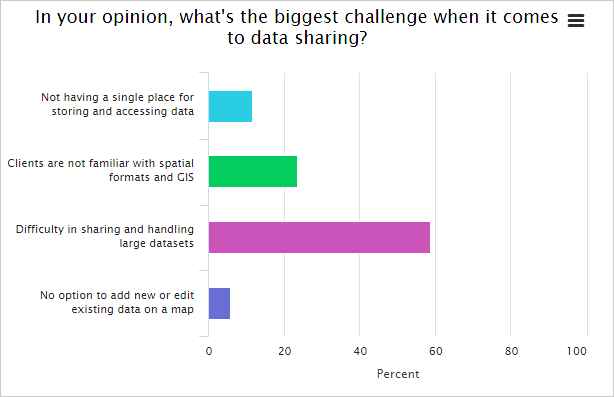
The poll from last year’s webinar about sharing rasters.
More than 50% of GIS users say that difficulty in sharing and handling large datasets is the most significant problem.
And it’s no wonder. Most companies only use desktop GIS software that shackles their ability to share rasters easily.
On top of that, the raster maps and drone images are probably scattered on several hard drives, memory sticks or even DVDs.
So, what’s the best practice to tackle these problems?
We think it’s adding an online GIS solution to your current desktop set-up or moving entirely to cloud-based software. Keep on reading and learn how GIS Cloud can help you get there.
Have all your raster maps and drone imagery in one place
As you already know, raster datasets are large and probably stored on several devices.
It is often the case in the drone mapping business, where the great potential of raster data rarely reaches its true potential, due to its size.
If you want to share maps seamlessly with collaborators and clients, they have to be located in one place, and that place is the cloud. Now, let’s see how you can get all your geospatial data centralized using GIS Cloud.
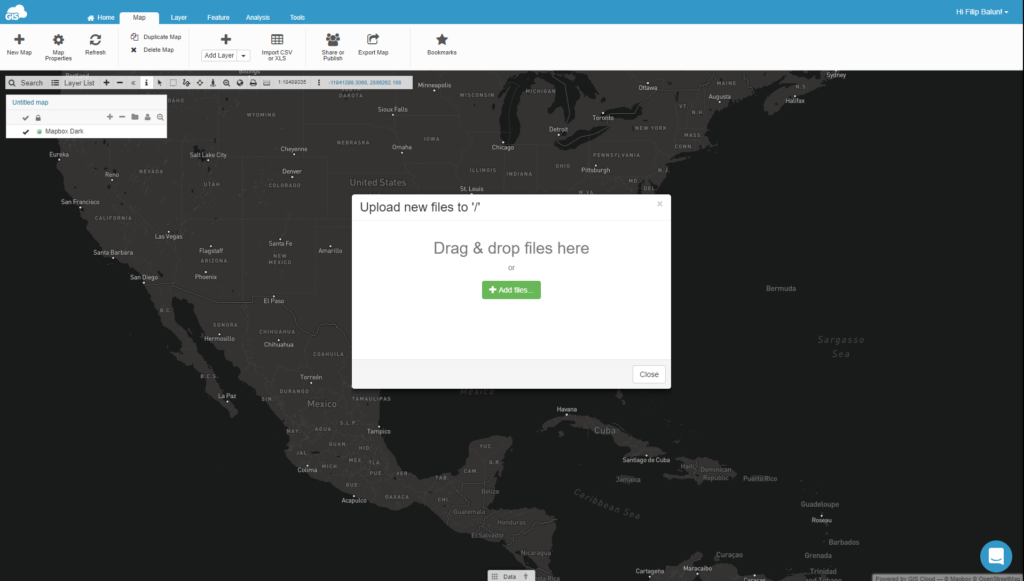
To upload the data, you need to use the Map Editor, a central application in the GIS Cloud suite.
The process is as easy as it gets:
- 1. Create a new map
- 2. Drag and drop a raster on a map (vectors also supported)
The data promptly visualizes and it’s ready for sharing and editing. You can also use this large rasters and drone images as basemaps.
However, most GIS users have a lot of spatial data and need an option for bulk upload. By using the file manager tool, you can upload significant amounts of data in no time. Then just create a map and add the uploaded raster or vector data.
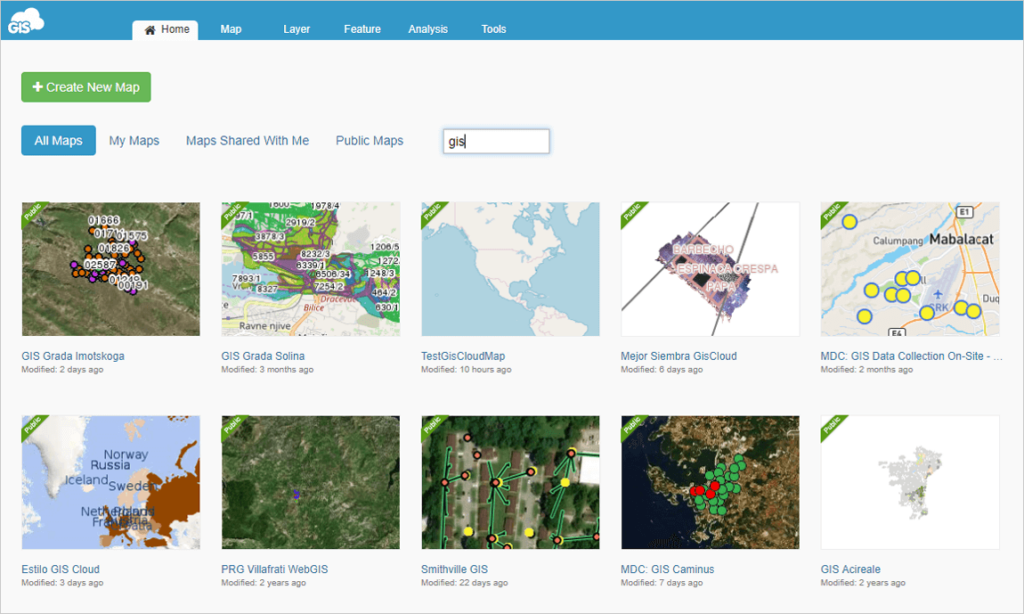
When you upload the data and everything is set up, your dashboard should look something like this.
As you can see, the maps are neatly laid out and ready for sharing.
Collaborators and Clients can view the raster maps online
A large amount of data in various formats is often difficult to distribute to a large number of users. Printed maps and large datasets on DVDs are slowing the information flow to the point of meaninglessness.
This data is often restricted only to the use of experienced GIS staff who know how to operate software necessary for working with mapping data.
Sharing raster maps and drone imagery online has many advantages. You can instantly share insights with a client and get direct feedback. Also, the only thing you need to view the data is a browser, be it on a smartphone, tablet or desktop.
Up to now, we have shown you how to centralize your raster data with GIS Cloud, now let’s cover the sharing aspect.
Sharing a map is easy, open it in Map Editor and share it with a user that has a license for the Map Viewer app. Any user who has a Map Editor license can also view privately shared maps.
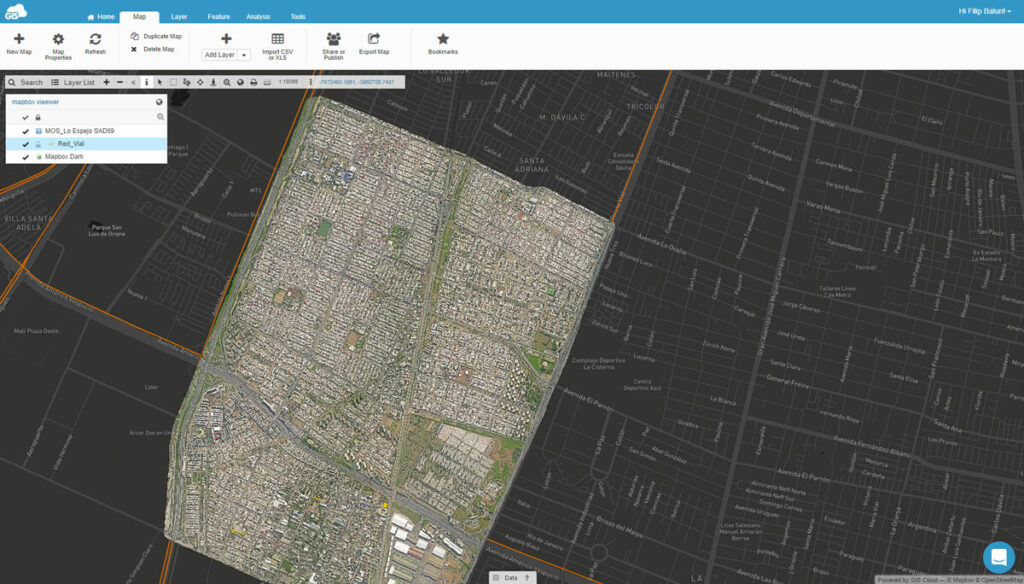
The Map Viewer is an app that gives users an easy way to view and access maps and data. It’s optimized for non-professionals and enables you to access shared or public maps on any device in real time.
Here’s how it looks when viewing a shared map.
It also allows you to share data in a controlled environment, allowing different levels of access to your clients by defining permissions (give access or restrict access).
Working on top of your raster maps and drone images
As we have mentioned earlier, you can use your rasters as basemaps. On top of the basemap you can use the Map Editor to edit spatial data and create points, lines and polygons, and also non-spatial data like pdf and photos that you can add to a map feature.
When the data is uploaded, you can perform spatial analysis. Use tools like hotspot, buffer, area & radius coverage to get the most out of your spatial data.
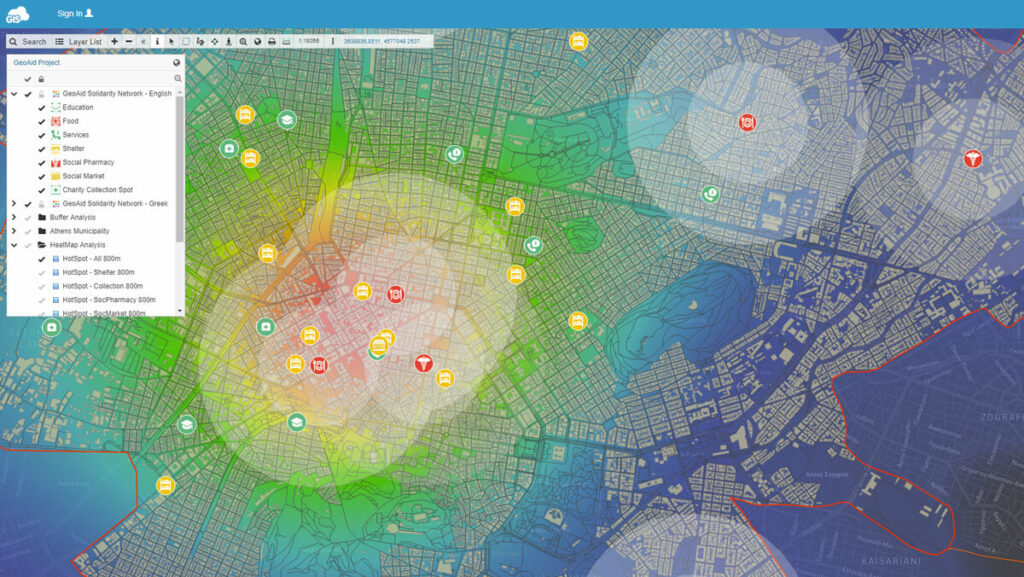
Heat map created with hotspot tool.
Another cool thing you can do is to populate the raster map with field data in real time. By using the Mobile Data Collection App, you can collect points, lines or polygons. Every data point collected instantly populates the map.
There’s a lot of stuff you can do with GIS Cloud. Explore all the features by signing up to the 30-day free trial.
Integrating raster data from desktop GIS tools
The fastest way to share raster and vector data from your desktop GIS setup is to integrate with GIS Cloud.
If you’re using ArcMap or QGIS, you can integrate the data easily.
GIS Cloud Publisher for ArcMap extension enables you to publish your maps from ArcMap to GIS Cloud. It automatically uploads your data, symbology, layer structure and spatial references.
The idea is that what you see in your desktop GIS is instantly replicated on your GIS Cloud account.
Once your maps and data are on GIS Cloud, they are easily shared to the public or embedded into your website.
All of the above also applies for the GIS Cloud Publisher for QGIS.
Use cases regarding high-resolution raster maps
Real-world examples are the best way to understand how GIS Cloud can help you when working with large rasters.
Mapping Land Usage With Drones To Build A Hospital Extension In Tanzania
The use case describes in detail how you can map land usage with drones. Learn how Engineers without borders completed this project by mapping hospital area with drones and using GIS Cloud to visualize high-resolution drone imagery, achieve real-time data editing and team collaboration.
Sharing The 3D Drone Mapping Imagery With Clients: A Report From South Africa
The project consists of mapping a large scale (600ha) development area in Hammarsdale, South Africa. 3DroneMapping staff had a task to use drones to produce high-resolution orthophotos and contours.
There are more interesting use cases you can explore on our company blog.
If you want to know more about GIS Cloud, don’t hesitate to contact us. Also, try out the 30-day free trial.